RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Exercise 6.2 Solutions: The word ‘geometry’ comes from the Greek words ‘geo’, meaning the ‘earth’, and ‘metrein’, meaning ‘to measure’. Geometry appears to have originated from the need for measuring land. This branch of mathematics was studied in various forms in every ancient civilization, be it in Egypt, Babylonia, China, India, Greece, the Incas, etc. The people of these civilizations faced several practical problems which required the development of geometry in various ways. Know more on Euclids Geometry.
Download RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Exercise 6.2 Solutions
RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Introduction To Euclids Geometry
Access The RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Exercise 6.2 Solutions
Question 1:
Draw the perpendiculars from the AF, BG, CH, DI and EJ on the x-axis.
(1) The distance of A from the y-axis = OF = -6 units
The distance of A from the x-axis = AF = 5 units
Hence, the coordinates of A are (-6, 5)
(2)The distance of B from the y-axis = OG = 5 units
The distance of B from the x-axis = BG = 4 units
Hence, the coordinate of B are (5, 4)
(3)The distance of C from the y-axis = OH = -3 units
The distance of C from the x-axis = HC = 2 units
Hence, the coordinate of C are (-3, 2)
(4)The distance of D from the y-axis = OI = 2 units
The distance of D from the x-axis = ID = -2 units
Hence, the coordinate of D are (2, -2)
(5)The distance of E from the y-axis = OJ = -1 unit
The distance of E from the x-axis = JE = -4 units
Hence, the coordinate of E are (-1, -4)
Thus, the coordinates of A, B, C, D and E are respectively, A(-6,5), B(5,4), C(-3,2), D(2,-2) and E(-1,-4)
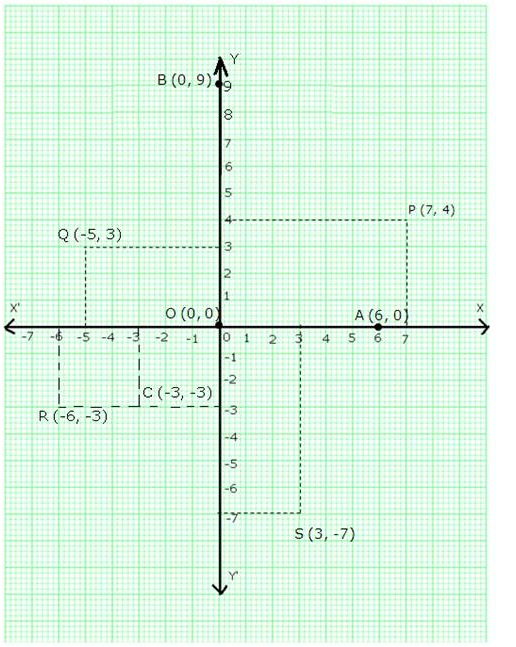
Question 2:
Let X’OX and Y’OY be the coordinate axes.
Fix the side of the small squares as one units.
(i) Starting from O, take +7 units on the x-axis and then +4 units on the y-axis to obtain the point P(7, 4)
(ii) Starting from O, take -5 units on the x-axis and then +3 units on the y-axis to obtain the point Q(-5, 3)
(iii) Starting from O, take -6 units on the x-axis and then -3 units on the y-axis to obtain the point R(-6, -3)
(iv) Starting from O, take +3 units on the x-axis and then -7 units on the y-axis to obtain the point S(3, -7)
(v) Starting from O, take 6 units on the x-axis to obtain the point A(6, 0)
(vi) Starting from O, take 9 units on the y-axis to obtain the point B(0,9)
(vii) Mark the point O as O(0, 0)
(viii) Starting from O, take -3 units on the x-axis and then -3 units on the y-axis to obtain the point C(-3, -3)
These points are shown in the following graph:
Question 3:
(i) In (7, 0), we have the ordinate = 0.
Therefore, (7,0) lies on the x-axis
(ii) In (0, -5), we have the abscissa = 0.
Therefore, (0,-5) lies on the y-axis
(iii) In (0,1), we have the abscissa = 0.
Therefore, (0,1) lies on the y-axis
(iv) In (-4,0), we have the ordinate = 0.
Therefore, (-4,0) lies on the x-axis
Question 4:
(i) Points of the type (-, +) lie in the second quadrant. Therefore, the point (-6,5) lies in the II quadrant.
(ii) Points of the type (-, -) lie in the third quadrant. Therefore, the point (-3,-2) lies in the III quadrant.
(iii) Points of the type (+, -) lie in the fourth quadrant. Therefore, the point (2,-9) lies in the IV quadrant.
Question 5:
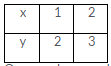
The given equation is y = x + 1
Putting x = 1, we get y = 1 + 1 = 2
Putting x = 2, we get y = 2 + 1 = 3
Thus, we have the following table:
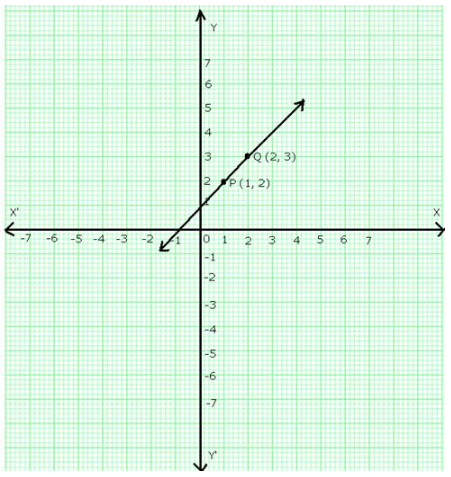
On a graph paper, draw the lines X’OX and YOY’ as the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Then, plot points P (1, 2) and Q (2, 3) on the graph paper. Join PQ and extend it to both sides.
Then, line PQ is the graph of the equation y = x + 1.
Question 6:
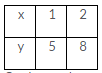
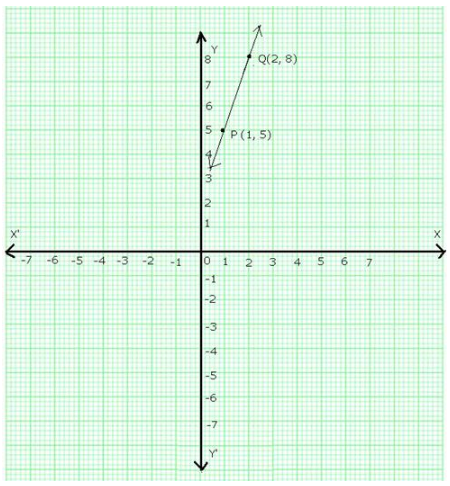
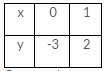
The give equation is y = 3x + 2
Putting x = 1, we get y = (3 1) + 2 = 5
Putting x = 2, we get y = (3 2) + 2 = 8
Thus, we have the following table:
On the graph paper, draw the lines X’OX and YOY’ as the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Now, plot points P(1,5) and Q(2,8) on the graph paper.
Join PQ and extend it to both sides.
Then, line PQ is the graph of the equation y = 3x + 2.
Question 7:
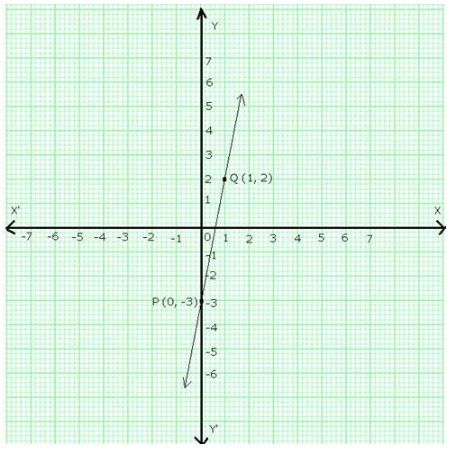
The given equation is y = 5x – 3
Putting x = 0, we get y = (5 × 0) – 3 = -3
Putting x = 1, we get y = (5 × 1) – 3 = 2
Thus, we have following table:
On a graph paper, draw the lines X’OX and YOY’ as the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Now plot the points P(0,-3) and Q(1,2).
Join PQ and extend it in both the directions.
Then, line PQ is the graph of the equation, y = 5x – 3.
Question 8:
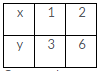
The given equation is y = 3x
Putting x = 1, we get y = (3 1) = 3
Putting x = 2, we get y = (3 2) = 6
Thus, we have the following table:
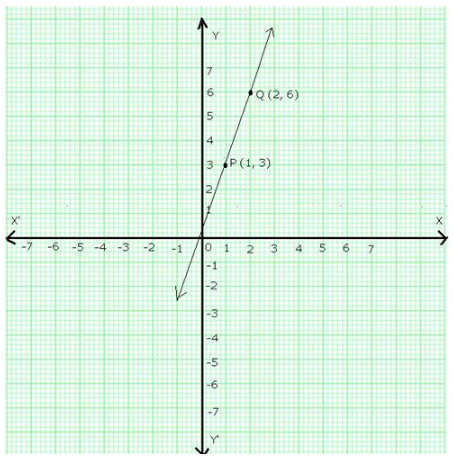
On a graph paper draw the lines X’OX and YOY’ as the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Now, plot points P(1,3) and Q(2,6).
Join PQ and extend it in both the directions.
Then, line PQ is the graph of the equation y = 3x.
Question 9:
The given equation is y = -x
Putting x = 1, we get y = -1
Putting x = 2, we get y = -2
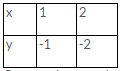
Thus, we have the following table:
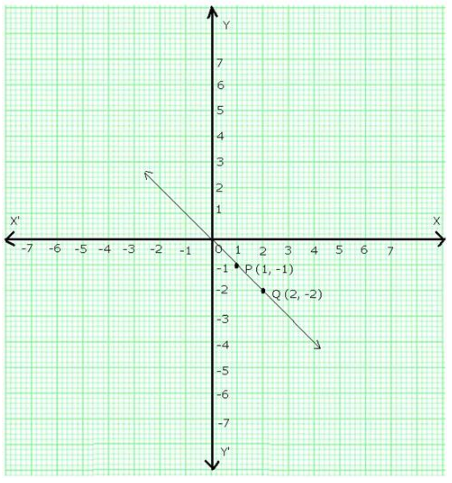
On a graph paper, draw the lines X’OX and YOY’ as the x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Now, plot the points P(1,-1) and Q(2,-2).
Join PQ and extend it in both directions.
Then, line PQ is the graph of the equation y = -x.
Important Definition for RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Ex 6b Solutions
- A line is an endless length.
- A point has no dimension (length, breadth, and width).
- A line that lies evenly with the points on itself is straight.
- Points are the ends of a line.
- A surface is that which has breadth and length only.
- A plane surface is a surface that lies evenly with straight lines on itself.
- Lines are the edges of a surface.
Know More at the official website.
FAQs on RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Exercise 6.2 Solutions
From where can I find the download link for the RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Exercise 6.2 Solutions PDF?
You can find the download link in the above blog.
How much does it cost to download the RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Exercise 6.2 Solutions PDF?
You can download it for free.
Can I access the RS Aggarwal Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths Exercise 6.2 Solutions PDF Offline?
Once you have downloaded the PDF online, you can access it offline whenever you want.