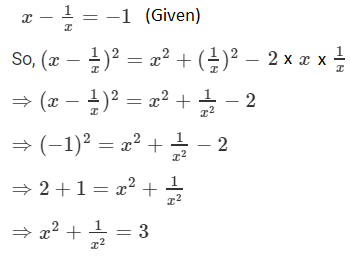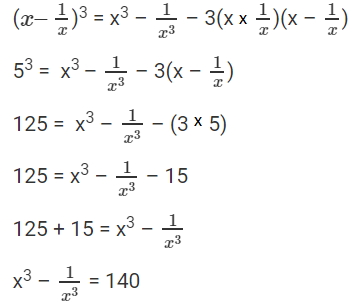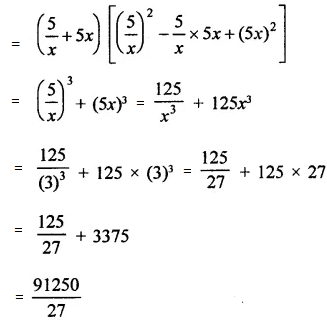RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 – Algebraic Identities: Have doubts with Mathematics exam preparation? Have you started looking for some good study material yet? If not, don’t worry, we bring you RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities for solving the confusion with Algebraic identities. To know more, read the whole blog.
Download RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities: PDF
RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4
RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities: Exercise-wise Solutions
Access answers of RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 – Algebraic Identities
Exercise 4.1 Page No: 4.6
Question 1: Evaluate each of the following using identities:
(i) (2x – 1/x)2
(ii) (2x + y) (2x – y)
(iii) (a2b – b2a)2
(iv) (a – 0.1) (a + 0.1)
(v) (1.5.x2 – 0.3y2) (1.5x2 + 0.3y2)
Solution:
(i) (2x – 1/x)2
[Use identity: (a – b)2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab ]
(2x – 1/x)2 = (2x)2 + (1/x)2 – 2 (2x)(1/x)
= 4x2 + 1/x2 – 4
(ii) (2x + y) (2x – y)
[Use identity: (a – b)(a + b) = a2 – b2 ]
(2x + y) (2x – y) = (2x )2 – (y)2
= 4x2 – y2
(iii) (a2b – b2a)2
[Use identity: (a – b)2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab ]
(a2b – b2a)2 = (a2b) 2 + (b2a)2 – 2 (a2b)( b2a)
= a4b 2 + b4a2 – 2 a3b3
(iv) (a – 0.1) (a + 0.1)
[Use identity: (a – b)(a + b) = a2 – b2 ]
(a – 0.1) (a + 0.1) = (a)2 – (0.1)2
= (a)2 – 0.01
(v) (1.5 x2 – 0.3y2) (1.5 x2 + 0.3y2)
[Use identity: (a – b)(a + b) = a2 – b2 ]
(1.5 x2 – 0.3y2) (1.5x2 + 0.3y2) = (1.5 x2 ) 2 – (0.3y2)2
= 2.25 x4 – 0.09y4
Question 2: Evaluate each of the following using identities:
(i) (399)2
(ii) (0.98)2
(iii) 991 x 1009
(iv) 117 x 83
Solution:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
Question 3: Simplify each of the following:
(i) 175 x 175 +2 x 175 x 25 + 25 x 25
(ii) 322 x 322 – 2 x 322 x 22 + 22 x 22
(iii) 0.76 x 0.76 + 2 x 0.76 x 0.24 + 0.24 x 0.24
(iv)
Solution:
(i) 175 x 175 +2 x 175 x 25 + 25 x 25 = (175)2 + 2 (175) (25) + (25)2
= (175 + 25)2
[Because a2+ b2+2ab = (a+b)2 ]
= (200)2
= 40000
So, 175 x 175 +2 x 175 x 25 + 25 x 25 = 40000.
(ii) 322 x 322 – 2 x 322 x 22 + 22 x 22
= (322)2 – 2 x 322 x 22 + (22)2
= (322 – 22)2
[Because a2+ b2-2ab = (a-b)2]
= (300)2
= 90000
So, 322 x 322 – 2 x 322 x 22 + 22 x 22= 90000.
(iii) 0.76 x 0.76 + 2 x 0.76 x 0.24 + 0.24 x 0.24
= (0.76) 2 + 2 x 0.76 x 0.24 + (0.24) 2
= (0.76+0.24) 2
[ Because a2+ b2+2ab = (a+b)2]
= (1.00)2
= 1
So, 0.76 x 0.76 + 2 x 0.76 x 0.24 + 0.24 x 0.24 = 1.
(iv)
Question 4: If x + 1/x = 11, find the value of x2 +1/x2.
Solution:
Question 5: If x – 1/x = -1, find the value of x2 +1/x2.
Solution:
Exercise 4.2 Page No: 4.11
Question 1: Write the following in the expanded form:
(i) (a + 2b + c)2
(ii) (2a − 3b − c)2
(iii) (−3x+y+z)2
(iv) (m+2n−5p)2
(v) (2+x−2y)2
(vi) (a2 +b2 +c2) 2
(vii) (ab+bc+ca) 2
(viii) (x/y+y/z+z/x)2
(ix) (a/bc + b/ac + c/ab) 2
(x) (x+2y+4z) 2
(xi) (2x−y+z) 2
(xii) (−2x+3y+2z) 2
Solution:
Using identities:
(x + y + z)2 = x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy + 2yz + 2xz
(i) (a + 2b + c)2
= a2 + (2b) 2 + c2 + 2a(2b) + 2ac + 2(2b)c
= a2 + 4b2 + c2 + 4ab + 2ac + 4bc
(ii) (2a − 3b − c)2
= [(2a) + (−3b) + (−c)]2
= (2a) 2 + (−3b) 2 + (−c) 2 + 2(2a)(−3b) + 2(−3b)(−c) + 2(2a)(−c)
= 4a2 + 9b2 + c2 − 12ab + 6bc − 4ca
(iii) (−3x+y+z)2
= [(−3x) 2 + y2 + z2 + 2(−3x)y + 2yz + 2(−3x)z
= 9x2 + y2 + z2 − 6xy + 2yz − 6xz
(iv) (m+2n−5p)2
= m2 + (2n) 2 + (−5p) 2 + 2m × 2n + (2×2n×−5p) + 2m × −5p
= m2 + 4n2 + 25p2 + 4mn − 20np − 10pm
(v) (2+x−2y)2
= 22 + x2 + (−2y) 2 + 2(2)(x) + 2(x)(−2y) + 2(2)(−2y)
= 4 + x2 + 4y2 + 4 x − 4xy − 8y
(vi) (a2 +b2 +c2) 2
= (a2) 2 + (b2) 2 + (c2 ) 2 + 2a2 b2 + 2b2c2 + 2a2c2
= a4 + b4 + c4 + 2a2 b2 + 2b2 c2 + 2c2 a2
(vii) (ab+bc+ca) 2
= (ab)2 + (bc) 2 + (ca) 2 + 2(ab)(bc) + 2(bc)(ca) + 2(ab)(ca)
= a2 b2 + b2c2 + c2 a2 + 2(ac)b2 + 2(ab)(c) 2 + 2(bc)(a) 2
(viii) (x/y+y/z+z/x)2
(ix) (a/bc + b/ac + c/ab) 2
(x) (x+2y+4z) 2
= x2 + (2y) 2 + (4z) 2 + (2x)(2y) + 2(2y)(4z) + 2x(4z)
= x2 + 4y2 + 16z2 + 4xy + 16yz + 8xz
(xi) (2x−y+z) 2
= (2x) 2 + (−y) 2 + (z) 2 + 2(2x)(−y) + 2(−y)(z) + 2(2x)(z)
= 4x2 + y2 + z2 − 4xy−2yz+4xz
(xii) (−2x+3y+2z) 2
= (−2x) 2 + (3y) 2 + ( 2z) 2 + 2(−2x)(3y)+2(3y)(2z)+2(−2x)(2z)
= 4x2 + 9y2 + 4z2 −12xy+12yz−8xz
Question 2: Simplify
(i) (a + b + c)2 + (a − b + c) 2
(ii) (a + b + c)2 − (a − b + c) 2
(iii) (a + b + c)2 + (a – b + c) 2 + (a + b − c) 2
(iv) (2x + p − c)2 − (2x − p + c) 2
(v) (x2 + y2 − z2) 2 − (x2 − y2 + z2) 2
Solution:
(i) (a + b + c)2 + (a − b + c) 2
= (a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab+2bc+2ca) + (a2 + (−b) 2 + c2 −2ab−2bc+2ca)
= 2a2 + 2 b2 + 2c2 + 4ca
(ii) (a + b + c)2 − (a − b + c) 2
= (a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab+2bc+2ca) − (a2 + (−b) 2 + c2 −2ab−2bc+2ca)
= a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca − a2 − b2 − c2 + 2ab + 2bc − 2ca
= 4ab + 4bc
(iii) (a + b + c)2 + (a – b + c) 2 + (a + b − c) 2
= a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca + (a2 + b2 + (c) 2 − 2ab − 2cb + 2ca) + (a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab − 2bc – 2ca)
= 3 a2 + 3b2 + 3c2 + 2ab − 2bc + 2ca
(iv) (2x + p − c)2 − (2x − p + c) 2
= [4x2 + p2 + c2 + 4xp − 2pc − 4xc] − [4x2 + p2 + c2 − 4xp− 2pc + 4xc]
= 4x2 + p2 + c2 + 4xp − 2pc − 4cx − 4x2 − p2 − c2 + 4xp + 2pc− 4cx
= 8xp − 8xc
= 8(xp − xc)
(v) (x2 + y2 − z2) 2 − (x2 − y2 + z2) 2
= (x2 + y2 + (−z) 2) 2 − (x2 − y2 + z2) 2
= [x4 + y4 + z4 + 2x2y2 – 2y2z 2 – 2x2z2 − [x4 + y4 + z4 − 2x2y2 − 2y2z2 + 2x2z2]
= 4x2y2 – 4z2x2
Question 3: If a + b + c = 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 = 16, find the value of ab + bc + ca.
Solution:
a + b + c = 0 and a2 + b2 + c2 = 16 (given)
Choose a + b + c = 0
Squaring both sides,
(a + b + c)2 = 0
a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(ab + bc + ca) = 0
16 + 2(ab + bc + c) = 0
2(ab + bc + ca) = -16
ab + bc + ca = -16/2 = -8
or ab + bc + ca = -8
Exercise 4.3 Page No: 4.19
Question 1: Find the cube of each of the following binomial expressions:
(i) (1/x + y/3)
(ii) (3/x – 2/x2)
(iii) (2x + 3/x)
(iv) (4 – 1/3x)
Solution:
[Using identities: (a + b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b) and (a – b)3 = a3 – b3 – 3ab(a – b) ]
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
Question 2: Simplify each of the following:
(i) (x + 3)3 + (x – 3) 3
(ii) (x/2 + y/3) 3 – (x/2 – y/3) 3
(iii) (x + 2/x) 3 + (x – 2/x) 3
(iv) (2x – 5y) 3 – (2x + 5y) 3
Solution:
[Using identities:
a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab)
a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab)
(a + b)(a-b) = a2 – b2
(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab and
(a – b)2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab]
(i) (x + 3)3 + (x – 3) 3
Here a = (x + 3), b = (x – 3)
(ii) (x/2 + y/3) 3 – (x/2 – y/3) 3
Here a = (x/2 + y/3) and b = (x/2 – y/3)
(iii) (x + 2/x) 3 + (x – 2/x) 3
Here a = (x + 2/x) and b = (x – 2/x)
(iv) (2x – 5y) 3 – (2x + 5y) 3
Here a = (2x – 5y) and b = 2x + 5y
Question 3: If a + b = 10 and ab = 21, find the value of a3 + b3.
Solution:
a + b = 10, ab = 21 (given)
Choose a + b = 10
Cubing both sides,
(a + b)3 = (10)3
a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b) = 1000
a3 + b3 + 3 x 21 x 10 = 1000 (using given values)
a3 + b3 + 630 = 1000
a3 + b3 = 1000 – 630 = 370
or a3 + b3 = 370
Question 4: If a – b = 4 and ab = 21, find the value of a3 – b3.
Solution:
a – b = 4, ab= 21 (given)
Choose a – b = 4
Cubing both sides,
(a – b)3 = (4)3
a3 – b3 – 3ab (a – b) = 64
a3 – b3 – 3 × 21 x 4 = 64 (using given values)
a3 – b3 – 252 = 64
a3 – b3 = 64 + 252
= 316
Or a3 – b3 = 316
Question 5: If x + 1/x = 5, find the value of x3 + 1/x3 .
Solution:
Given: x + 1/x = 5
Apply Cube on x + 1/x
Question 6: If x – 1/x = 7, find the value of x3 – 1/x3 .
Solution:
Given: x – 1/x = 7
Apply Cube on x – 1/x
Question 7: If x – 1/x = 5, find the value of x3 – 1/x3 .
Solution:
Given: x – 1/x = 5
Apply Cube on x – 1/x
Question 8: If (x2 + 1/x2) = 51, find the value of x3 – 1/x3.
Solution:
We know that: (x – y)2 = x2 + y2 – 2xy
Replace y with 1/x, we get
(x – 1/x)2 = x2 + 1/x2 – 2
Since (x2 + 1/x2) = 51 (given)
(x – 1/x)2 = 51 – 2 = 49
or (x – 1/x) = ±7
Now, Find x3 – 1/x3
We know that, x3 – y3 = (x – y)(x2 + y2 + xy)
Replace y with 1/x, we get
x3 – 1/x3 = (x – 1/x)(x2 + 1/x2 + 1)
Use (x – 1/x) = 7 and (x2 + 1/x2) = 51
x3 – 1/x3 = 7 x 52 = 364
x3 – 1/x3 = 364
Question 9: If (x2 + 1/x2) = 98, find the value of x3 + 1/x3.
Solution:
We know that: (x + y)2 = x2 + y2 + 2xy
Replace y with 1/x, we get
(x + 1/x)2 = x2 + 1/x2 + 2
Since (x2 + 1/x2) = 98 (given)
(x + 1/x)2 = 98 + 2 = 100
or (x + 1/x) = ±10
Now, Find x3 + 1/x3
We know that, x3 + y3 = (x + y)(x2 + y2 – xy)
Replace y with 1/x, we get
x3 + 1/x3 = (x + 1/x)(x2 + 1/x2 – 1)
Use (x + 1/x) = 10 and (x2 + 1/x2) = 98
x3 + 1/x3 = 10 x 97 = 970
x3 + 1/x3 = 970
Question 10: If 2x + 3y = 13 and xy = 6, find the value of 8x3 + 27y3.
Solution:
Given: 2x + 3y = 13, xy = 6
Cubing 2x + 3y = 13 both sides, we get
(2x + 3y)3 = (13)3
(2x)3 + (3y) 3 + 3( 2x )(3y) (2x + 3y) = 2197
8x3 + 27y3 + 18xy(2x + 3y) = 2197
8x3 + 27y3 + 18 x 6 x 13 = 2197
8x3 + 27y3 + 1404 = 2197
8x3 + 27y3 = 2197 – 1404 = 793
8x3 + 27y3 = 793
Question 11: If 3x – 2y= 11 and xy = 12, find the value of 27x3 – 8y3.
Solution:
Given: 3x – 2y = 11 and xy = 12
Cubing 3x – 2y = 11 both sides, we get
(3x – 2y)3 = (11)3
(3x)3 – (2y)3 – 3 ( 3x)( 2y) (3x – 2y) =1331
27x3 – 8y3 – 18xy(3x -2y) =1331
27x3 – 8y3 – 18 x 12 x 11 = 1331
27x3 – 8y3 – 2376 = 1331
27x3 – 8y3 = 1331 + 2376 = 3707
27x3 – 8y3 = 3707
Exercise 4.4 Page No: 4.23
Question 1: Find the following products:
(i) (3x + 2y)(9x2 – 6xy + 4y2)
(ii) (4x – 5y)(16x2 + 20xy + 25y2)
(iii) (7p4 + q)(49p8 – 7p4q + q2)
(iv) (x/2 + 2y)(x2/4 – xy + 4y2)
(v) (3/x – 5/y)(9/x2 + 25/y2 + 15/xy)
(vi) (3 + 5/x)(9 – 15/x + 25/x2)
(vii) (2/x + 3x)(4/x2 + 9x2 – 6)
(viii) (3/x – 2x2)(9/x2 + 4x4 – 6x)
(ix) (1 – x)(1 + x + x2)
(x) (1 + x)(1 – x + x2)
(xi) (x2 – 1)(x4 + x2 +1)
(xii) (x3 + 1)(x6 – x3 + 1)
Solution:
(i) (3x + 2y)(9x2 – 6xy + 4y2)
= (3x + 2y)[(3x)2 – (3x)(2y) + (2y)2)]
We know, a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab)
= (3x)3 + (2y) 3
= 27x3 + 8y3
(ii) (4x – 5y)(16x2 + 20xy + 25y2)
= (4x – 5y)[(4x)2 + (4x)(5y) + (5y)2)]
We know, a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab)
= (4x)3 – (5y) 3
= 64x3 – 125y3
(iii) (7p4 + q)(49p8 – 7p4q + q2)
= (7p4 + q)[(7p4)2 – (7p4)(q) + (q)2)]
We know, a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab)
= (7p4)3 + (q) 3
= 343 p12 + q3
(iv) (x/2 + 2y)(x2/4 – xy + 4y2)
We know, a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab)
(x/2 + 2y)(x2/4 – xy + 4y2)
(v) (3/x – 5/y)(9/x2 + 25/y2 + 15/xy)
[Using a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab) ]
(vi) (3 + 5/x)(9 – 15/x + 25/x2)
[Using: a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab)]
(vii) (2/x + 3x)(4/x2 + 9x2 – 6)
[Using: a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab)]
(viii) (3/x – 2x2)(9/x2 + 4x4 – 6x)
[Using : a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab)]
(ix) (1 – x)(1 + x + x2)
And we know, a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab)
(1 – x)(1 + x + x2) can be written as
(1 – x)[(12 + (1)(x)+ x2)]
= (1)3 – (x)3
= 1 – x3
(x) (1 + x)(1 – x + x2)
And we know, a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab)]
(1 + x)(1 – x + x2) can be written as,
(1 + x)[(12 – (1)(x) + x2)]
= (1)3 + (x) 3
= 1 + x3
(xi) (x2 – 1)(x4 + x2 +1) can be written as,
(x2 – 1)[(x2)2 – 12 + (x2)(1)]
= (x2)3 – 13
= x6 – 1
[using a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab) ]
(xii) (x3 + 1)(x6 – x3 + 1) can be written as,
(x3 + 1)[(x3)2 – (x3)(1) + 12]
= (x3) 3 + 13
= x9 + 1
[using a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab) ]
Question 2: If x = 3 and y = -1, find the values of each of the following using in identity:
(i) (9y2 – 4x2)(81y4 + 36x2y2 + 16x4)
(ii) (3/x – x/3)(x2 /9 + 9/x2 + 1)
(iii) (x/7 + y/3)(x2/49 + y2/9 – xy/21)
(iv) (x/4 – y/3)(x2/16 + xy/12 + y2/9)
(v) (5/x + 5x)(25/x2 – 25 + 25x2)
Solution:
(i) (9y2 – 4x2)(81y4 + 36x2y2 + 16x4)
= (9y2 – 4x2) [(9y2 ) 2 + 9y2 x 4x2 + (4x2) 2 ]
= (9y2 ) 3 – (4x2)3
= 729 y6 – 64 x6
Put x = 3 and y = -1
= 729 – 46656
= – 45927
(ii) Put x = 3 and y = -1
(3/x – x/3)(x2 /9 + 9/x2 + 1)
(iii) Put x = 3 and y = -1
(x/7 + y/3)(x2/49 + y2/9 – xy/21)
(iv) Put x = 3 and y = -1
(x/4 – y/3)(x2/16 + xy/12 + y2/9)
(v) Put x = 3 and y = -1
(5/x + 5x)(25/x2 – 25 + 25x2)
Question 3: If a + b = 10 and ab = 16, find the value of a2 – ab + b2 and a2 + ab + b2.
Solution:
a + b = 10, ab = 16
Squaring, a + b = 10, both sides
(a + b)2 = (10)2
a2 + b2 + 2ab = 100
a2 + b2 + 2 x 16 = 100
a2 + b2 + 32 = 100
a2 + b2 = 100 – 32 = 68
a2 + b2 = 68
Again, a2 – ab + b2 = a2 + b2 – ab = 68 – 16 = 52 and
a2 + ab + b2 = a2 + b2 + ab = 68 + 16 = 84
Question 4: If a + b = 8 and ab = 6, find the value of a3 + b3.
Solution:
a + b = 8, ab = 6
Cubing, a + b = 8, both sides, we get
(a + b)3 = (8)3
a3 + b3 + 3ab(a + b) = 512
a3 + b3 + 3 x 6 x 8 = 512
a3 + b3 + 144 = 512
a3 + b3 = 512 – 144 = 368
a3 + b3 = 368
Exercise 4.5 Page No: 4.28
Question 1: Find the following products:
(i) (3x + 2y + 2z) (9x2 + 4y2 + 4z2 – 6xy – 4yz – 6zx)
(ii) (4x – 3y + 2z) (16x2 + 9y2 + 4z2 + 12xy + 6yz – 8zx)
(iii) (2a – 3b – 2c) (4a2 + 9b2 + 4c2 + 6ab – 6bc + 4ca)
(iv) (3x -4y + 5z) (9x2 + 16y2 + 25z2 + 12xy- 15zx + 20yz)
Solution:
(i) (3x + 2y + 2z) (9x2 + 4y2 + 4z2 – 6xy – 4yz – 6zx)
= (3x + 2y + 2z) [(3x)2 + (2y) 2 + (2z) 2 – 3x x 2y – 2y x 2z – 2z x 3x]
= (3x)3 + (2y)3 + (2z)3 – 3 x 3x x 2y x 2z
= 27x3 + 8y3 + 8Z3 – 36xyz
(ii) (4x – 3y + 2z) (16x2 + 9y2 + 4z2 + 12xy + 6yz – 8zx)
= (4x -3y + 2z) [(4x)2 + (-3y) 2 + (2z) 2 – 4x x (-3y) – (-3y) x (2z) – (2z x 4x)]
= (4x) 3 + (-3y) 3 + (2z) 3 – 3 x 4x x (-3y) x (2z)
= 64x3 – 27y3 + 8z3 + 72xyz
(iii) (2a -3b- 2c) (4a2 + 9b2 + 4c2 + 6ab – 6bc + 4ca)
= (2a -3b- 2c) [(2a) 2 + (-3b) 2 + (-2c) 2 – 2a x (-3b) – (-3b) x (-2c) – (-2c) x 2a]
= (2a)3 + (-3b) 3 + (-2c) 3 -3x 2a x (-3 b) (-2c)
= 8a3 – 21b3 – 8c3 – 36abc
(iv) (3x – 4y + 5z) (9x2 + 16y2 + 25z2 + 12xy – 15zx + 20yz)
= [3x + (-4y) + 5z] [(3x) 2 + (-4y) 2 + (5z) 2 – 3x x (-4y) -(-4y) (5z) – 5z x 3x]
= (3x) 3 + (-4y) 3 + (5z) 3 – 3 x 3x x (-4y) (5z)
= 27x3 – 64y3 + 125z3 + 180xyz
Question 2: If x + y + z = 8 and xy + yz+ zx = 20, find the value of x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz.
Solution:
We know, x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz = (x + y + z) (x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx)
Squaring, x + y + z = 8 both sides, we get
(x + y + z)2 = (8) 2
x2 + y2 + z2 + 2(xy + yz + zx) = 64
x2 + y2 + z2 + 2 x 20 = 64
x2 + y2 + z2 + 40 = 64
x2 + y2 + z2 = 24
Now,
x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz = (x + y + z) [x2 + y2 + z2 – (xy + yz + zx)]
= 8(24 – 20)
= 8 x 4
= 32
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz = 32
Question 3: If a +b + c = 9 and ab + bc + ca = 26, find the value of a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc.
Solution:
a + b + c = 9, ab + bc + ca = 26
Squaring, a + b + c = 9 both sides, we get
(a + b + c)2 = (9)2
a2 + b2 + c2 + 2 (ab + bc + ca) = 81
a2 + b2 + c2 + 2 x 26 = 81
a2 + b2 + c2 + 52 = 81
a2 + b2 + c2 = 29
Now, a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc = (a + b + c) [(a2 + b2 + c2 – (ab + bc + ca)]
= 9[29 – 26]
= 9 x 3
= 27
⇒ a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc = 27
Exercise VSAQs Page No: 4.28
Question 1: If x + 1/x = 3, then find the value of x2 + 1/x2.
Solution:
x + 1/x = 3
Squaring both sides, we have
(x + 1/x)2 = 32
x2 + 1/x2 + 2 = 9
x2 + 1/x2 = 9 – 2 = 7
Question 2: If x + 1/x = 3, then find the value of x^6 + 1/x^6.
Solution:
x + 1/x = 3
Squaring both sides, we have
(x + 1/x)2 = 32
x2 + 1/x2 + 2 = 9
x2 + 1/x2 = 9 – 2 = 7
x2 + 1/x2 = 7 …(1)
Cubing equation (1) both sides,
Question 3: If a + b = 7 and ab = 12, find the value of a2 + b2.
Solution:
a + b = 7, ab = 12
Squaring, a + b = 7, both sides,
(a + b) 2 = (7) 2
a2 + b2 + 2ab = 49
a2 + b2 + 2 x 12 = 49
a2 + b2 + 24 = 49
a2 + b2 = 25
Question 4: If a – b = 5 and ab = 12, find the value of a2 + b2.
Solution:
a – b = 5, ab = 12
Squaring, a – b = 5, both sides,
(a – b)2 = (5)2
a2 + b2 – 2ab = 25
a2 + b2 – 2 x 12 = 25
a2 + b2 – 24 = 25
a2 + b2 = 49
RD Sharma Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities
In the 4th Chapter of Class 9 RD Sharma Solutions, students will study important identities, as listed below.
- Algebraic identities introduction
- Identity for the square of a trinomial
- Sum and difference of cubes identity
These books are widely used by students to score high in the final exam. For RD Sharma Class 9 Maths Solutions, students can visit BYJU’S website and access step-by-step answers to all the questions provided in the RD Sharma textbook.
Important Topics: RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4
Important topics always let you run a thorough check on the titles that are there in the chapters. So, the important topics that the chapter includes are-
- Algebraic Identities Introduction
- Identity for the square of a trinomial
- Sum and difference of cubes Identity
Here is everything that students need to smoothly finish their CBSE Class 9 Mathematics syllabus. Start with CBSE Class 9 to build a solid future ahead. For any doubts, ask in the comments.
FAQs on RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 – Algebraic Identities
Can I access the RD Sharma Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 PDF offline?
Once you have downloaded the PDF online, you can access it offline as well.
From where can I download the PDF of RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 4?
You can find the download link from the above blog.
How much does it cost to download the PDF of RD Sharma Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4?
You can download it for free.