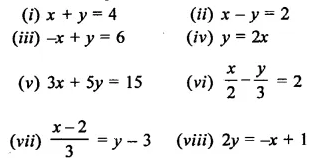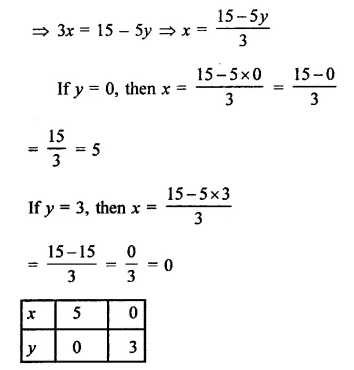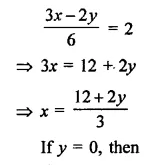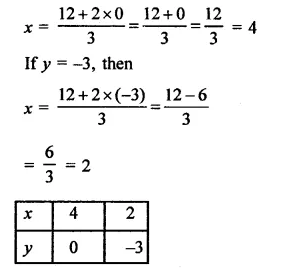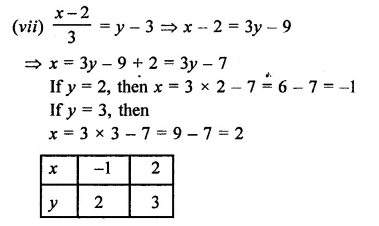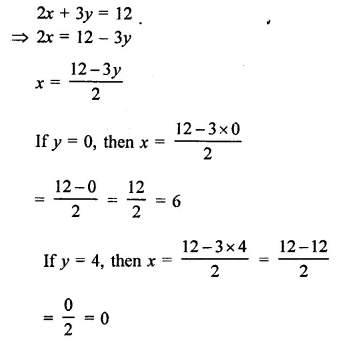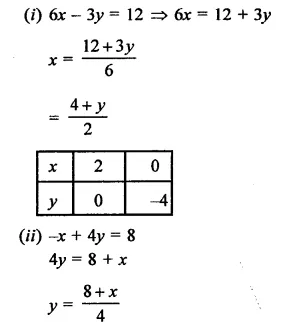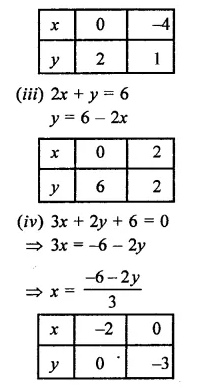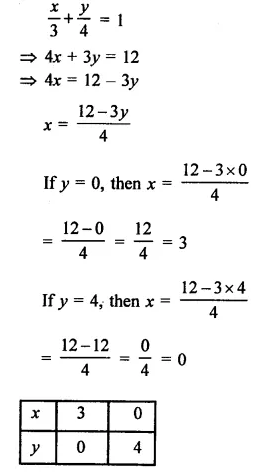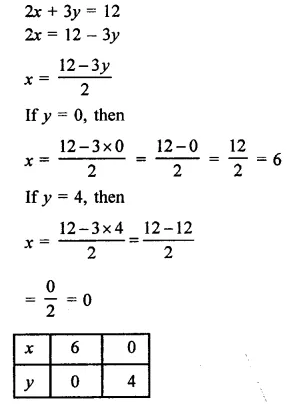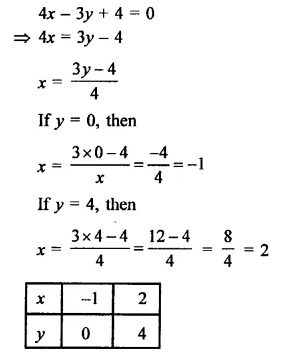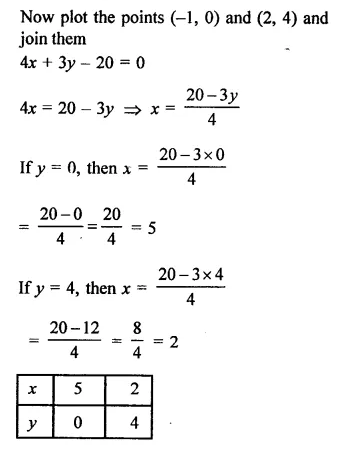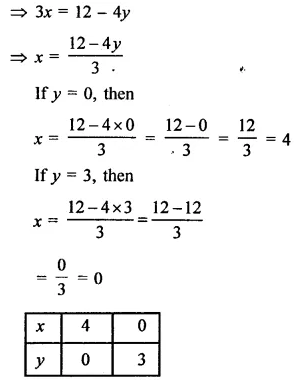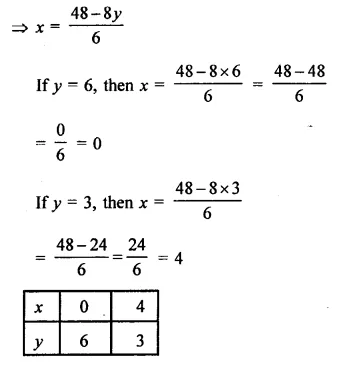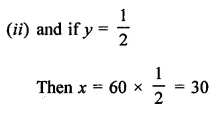RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3: It is very easy to learn and understand the concepts of Class 9 Maths when you have RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths. All the solutions are designed by our subject matter experts for your better understanding. To know more about the RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3, read the whole blog.
Access answers of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3
Question 1.
Draw the graph of each of the following linear equations in two variables.
Solution:
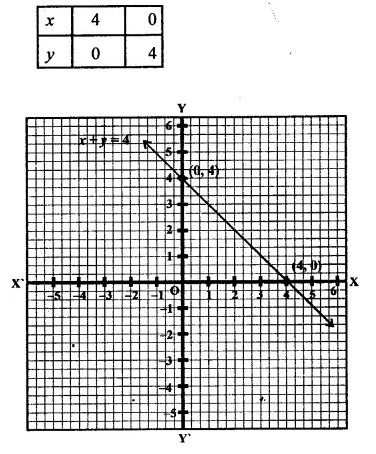
(i)x + y = 4
x = 4 – y
If y = 0, then x = 4
If y = 4, then x = 0
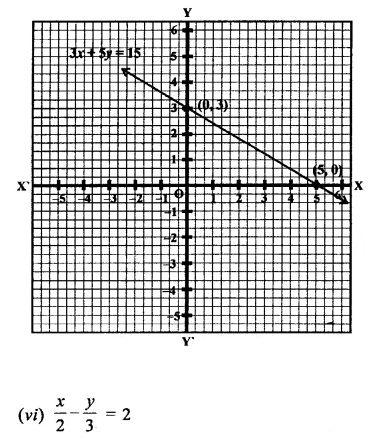
Now plot the points (4, 0) and (0, 4) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the given equation
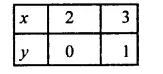
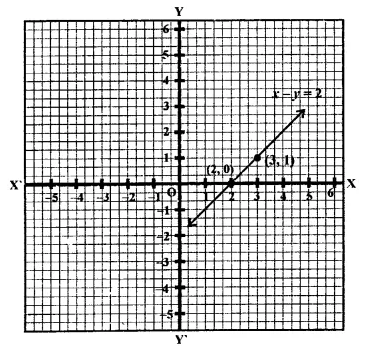
(ii)x – y = 2
x = 2 +y
If y = 0, then x = 2 and if y = 1,
Then x = 2 + 1 = 3
Now plot the points (2, 0) and (3, 1) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the equation.
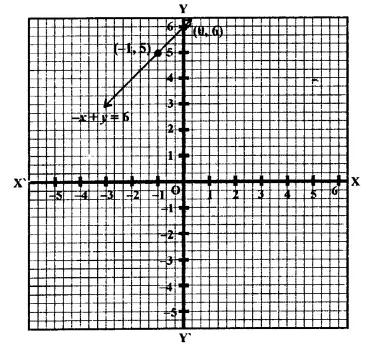
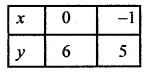
(iii) -x+y = 6 ⇒ y = 6+x
If x = 0, then y = 6 + 0 = 6
If x = -1, then y = 6 – 1 = 5
Now plot the points (0, 6) and (-1, 5) on the graph and join them to get a graph of the line.
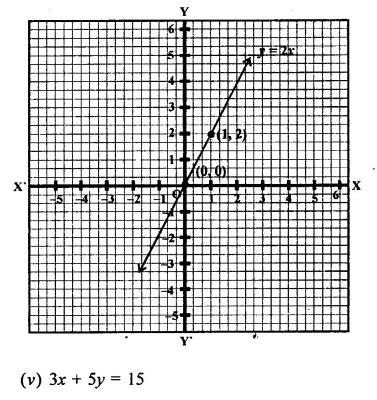
(iv) y = 2x
If x = 0, then y = 2 x 0 = 0
If x = 1, then y = 2 x 1 = 2
Now plot the points (0, 0) and (1, 2) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the line.
Now plot the points (5, 0) and (0, 3) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the line.
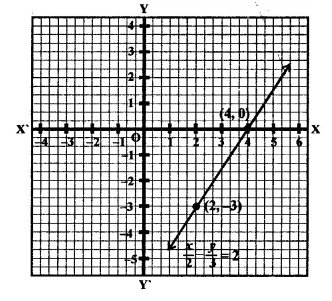
Now plot the points (4, 0) and (2, -3) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the line.
Now plot the points (-1, 2) and (2, 3) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the line.
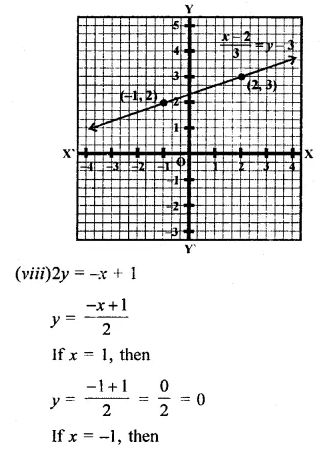
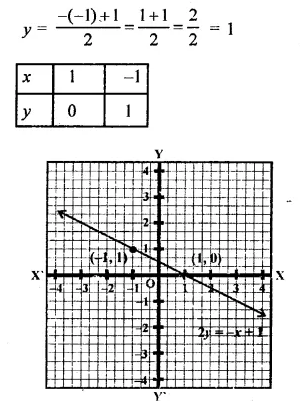
Now plot the points (1, 0) and (-1, 1) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the line.
Question 2.
Give the equations of two lines passing through (3, 12). How many more such lines are there, and why?
Solution:
∵ Points (3, 12) lie on the lines passing through the points
∴ Solutions is x = 3,y- 12
∴ The possible equation can be
x + y = 15
-x+y = 9
4x-y = 0
3x – y + 3 = 0
Question 3.
A three-wheeler scooter charges ₹15 for the first kilometer and ₹8 each for every subsequent kilometer. For a distance of x km, an amount of ₹y is paid. Write the linear equation representing the above information.
Solution:
Charges for the first kilometer = ₹15
Charges for next 1 km = ₹8
Distance = x km
and total amount = ₹y
∴ The linear equation will be,
15 + (x- 1) x 8 =y
⇒ 15 + 8x – 8 = y
⇒ 7 + 8x = y
∴ y = 8x + 7
Question 4.
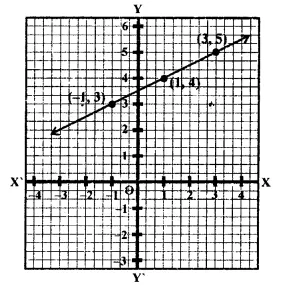
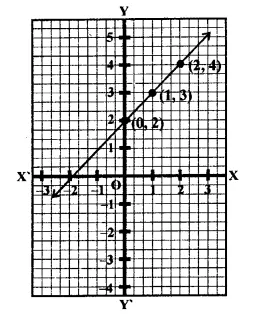
Plot the points (3, 5) and (-1, 3) on graph paper and verify that the straight line passing through these points also passes through the point (1, 4).
Solution:
Points (3, 5) and (-1, 3) have been plotted on the graph and joined to get a line. We see that die point (1,4) also lies out.
Question 5.
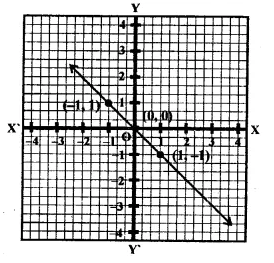
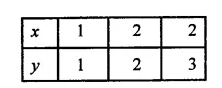
From the choices given below, choose the equation whose graph is given in the figure.
(i) y = x
(ii) x + y = 0
(iii) y = 2x
(iv) 2 + 3y = 7x
Solution:
From the graph, we see that Points (-1, 1) and (1, -1) are on the graph of the line these will satisfy the equation of the line
∴ -x = y ⇒ x+ y = 0
i.e., the required equation
∵ x + y = 0 is the graph of the equation.
Question 6.
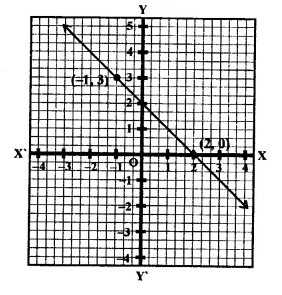
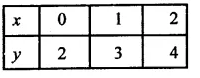
From the choices given below, choose the equation whose graph is given in the figure.
(i) y = x + 2
(ii) y = x – 2
(ii) y = -x + 2
(iv) x + 2y = 6
Solution:
From the graph
Points (-1,3) and (2, 0) lie on the graph of the line
Now these points, by observation, satisfy the equation y= -x+2
∴ The required equation is y = -x + 2 whose graph is given.
Question 7.
If the point (2, -2) lies on the graph of the linear equation 5x + ky =4, find the value of k.
Solution:
∵ Point (2, -2) lies on the graph of the linear equation 5x + ky = 4
∴ It will satisfy it
∴ Now substituting the values of x and y 5 x 2 + k (-2) = 4
⇒ 10 – 2k = 4 ⇒ -2k = 4 – 10 = -6 -6
⇒ k= −6−2 =3
Hence k = 3
Question 8.
Draw the graph of the equation 2x + 3p = 12. From the graph find the coordinates of the point.
(i) whose y -coordinates are 3
(ii) whose x-coordinates are -3
Solution:
Plot the points (6, 0) and (0, 4) on the graph and join them to get the graph of the line.
(i) If y = 3, then draw a perpendicular from y = 3 to the line, which gets meets it at P then the x-coordinate of p will be
∴ coordinates of P are ( 32,3)
(ii) If x = -3, draw perpendicular from x = -3 to the line, which meets it Q.
The y coordinates of Q will be y = 6
∴ co-ordinates of Q are (-3, 6)
Question 9.
Draw the graph of each of the equations given below. Also, find the coordinates of the points where the graph cuts the coordinates axes:
(i) 6x – 3y = 12
(ii) -x + 4y = 8
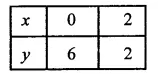
(iii) 2x + y = 6
(iv) 3x + 2y + 6 = 0
Solution:
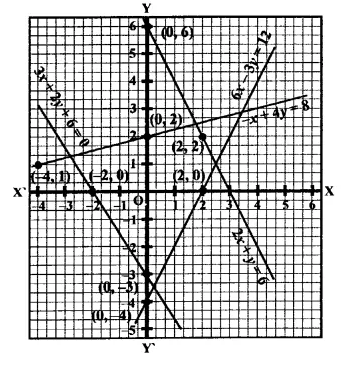
Now plot the points of each equation and join then we get four lines as shown on the graphs.
Equation (i) cuts the axes at (2, 0) and (0, -4)
Equation (ii) cuts the axes at (-8, 0) and (0, 2)
Equation (iii) cuts the axes at (3, 0), (0, 6) and
Equation (iv), cuts the axes at (-2, 0) and (0,-3)
Question 10.
A lending library has fixed charges for the first three days and an additional charge for each day thereafter. Aarushi paid ₹27 for a book kept for seven days. If fixed charges are ₹x and per day charges are ₹y. Write the linear equation representing the above information.
Solution:
Let fixed charges for the first 3 days = ₹x
and additional charges for each day = ₹y
Total period = 7 days
and amount charges = ₹27
∴ x + (7 – 3) x y = 27
⇒ x + 4y = 27
Hence x + 4y = 27
Question 11.
A number is 27 more than the number obtained by reversing its digits. If its unit’s and ten’s digits are x and y respectively, write the linear equation representing the above statement.
Solution:
Let the unit’s digit = x
and tens digit = y
∴ Number = x + 10y
By reversing the digits, units digit = y
and ten’s digit = x
∴ number = y + 10x
Now difference of these two numbers = 27 (x + 10y) – (y +10x) = 27
x + 10y – y – 10x = 27
⇒ -9x + 9y – 27 = 0
⇒ x-_y + 3 = 0 (Dividing by -9)
Hence equation is x – y + 3 = 0
Question 12.
The sum of a two-digit number and the number obtained by reversing the order of its digits is 121. If units and ten digits of the number are x and y respectively, then write the linear equation representing the above statement.
Solution:
Let unit digit = x
and tens digit = y
∴ Number = x + 10y
By reversing the digits,
units digit = y
and tens digit = x
∴ Number =y+ 10x
Now sum of these two numbers = 121
∴ x + 10y + y + 10x = 121
⇒ 1 lx + 11y = 121
⇒ x + y = 11 (Dividing by 11)
∴ x + y = 11
Question 13.
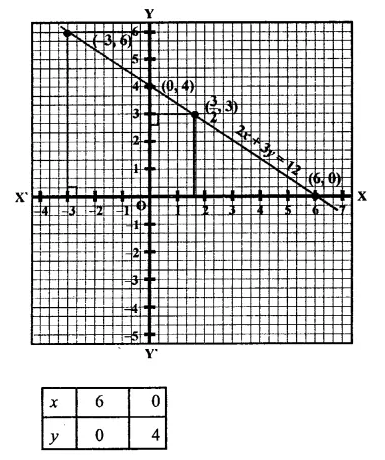
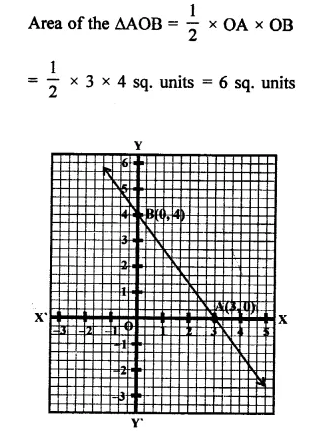
Draw the graph of the equation 2x + y = 6. Shade the region bounded by the graph and the coordinate axes. Also, find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:
2x + y = 6
⇒ y = 6 – 2x
If x = 0, then y = 6- 2 x 0 = 6 – 0 = 6
If x = 2, then y = 6- 2 x 2 = 6- 4 = 2
Now plot the points (0, 6) and (2, 2) on the graph and join them to get a line that intersects the x-axis at (3, 0) and the y-axis at (0,6)
Now coordinates if vertices of the shaded portion are (6, 0) (0, 0) and (3, 0) Now the area of the shaded region.
Question 14.
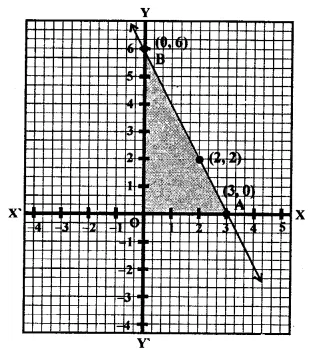
Draw the graph of the equation x3 + y4 = 1 Also find the area of the triangle formed by the line and the coordinate axes.
Solution:
Now plot the points (3, 0) and (0, 4) and join them to get a line with interests x-axis at A (3, 0) and y-axis at B (0, 4)
Question 15.
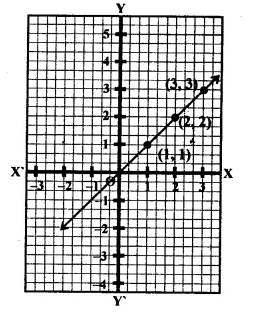
Draw the graph of y = | x |
Solution:
y = | x |
⇒ y = x [∵ | x |=x]
∴ Now taking z points.
Now plot the points (1, 1) (2, 2), and (3, 3) and join them to get a graph of a line.
Question 16.
Draw the graph of y = | x | + 2
Solution:
y – | x | + 2
⇒ y = x + 2 [| x | = x]
If x = 0, then y = 0 + 2 = 2
If x = 1, then y = 1+2 = 3
If x = 2, then y = 2 + 2 = 4
Now plot the points (0, 2), (1, 3), and (2, 4) on the graph and join them to get a line.
Question 17.
Draw the graphs of the following linear equation on the same graph paper.
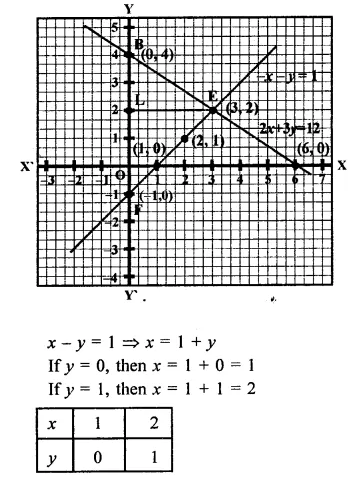
2x + 3y = 12, x -y = 1
Find the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by the two straight lines and the y-axis. Also, find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
Now plot the points (6, 0) (0, 4) on the graph to get a line.
Now plot the points (1, 0) and (2, 1) on the graph to get another line.
Area of the triangle FEB so formed,
= 12 FB x FL = 12 x 5 x 3
= 152
= 7.5 sq. units
co-ordinates of E, F, B are E (3, 2), (0, -1) and (0, 4)
Question 18.
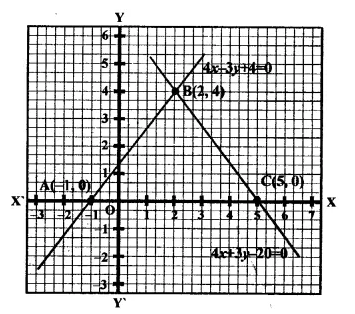
Draw the graphs of the linear equations 4x – 3y + 4 = 0 and 4x + 3y – 20 = 0. Find the area bounded by these lines and the x-axis.
Solution:
Now plot the points (5, 0) and (2, 4)and join them to get a line we see that the ΔABC is formed by bounding their line with the x-axis.
Question 19.
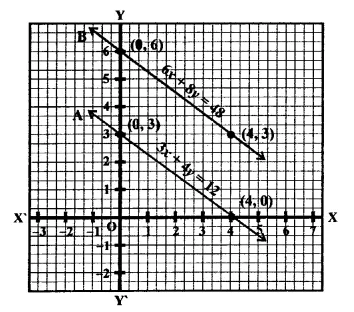
The path of a train A is given by the equation 3x + 4y – 12 = 0 and the path of another train B is given by the equation 6jc + 8y – 48 = 0. Represent this situation graphically.
Solution:
Path of the train A = 3x + 4y – 12 = 0
Path of the train B = 6x + 8y – 48 = 0
Now, 3x + 4y – 12 = 0
Now plot the points (4, 0) and (0, 3) on the graph and join them to get a line and 6x + 8y – 48 = 0
⇒ 6x = 48 – 8y
Now plot the points (0, 6) and (4, 3) on the graph and join them to get another line.
Question 20.
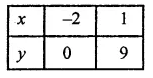
Ravish tells his daughter Aarushi, “Seven years ago, I was seven times as old as you were then. Also, three years from now, I shall be three times as old as you will be”. If the present ages of Aarushi and Ravish are x and y years respectively, represent this situation algebraically as well as graphically.
Solution:
The present age of Aarushi = x years
and age of Ravish = y years
7 years ago,
age of Aarushi = x – 7
years and age of Ravish =y-7 years
∴ y- 7 = 7 (X – 7)
⇒ y – 7 = 7x – 49
⇒ 7x – y = -7 + 49 = 42
7x – y = 42
⇒ y = 7x – 42
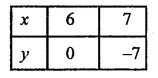
If x = 6, then
y = 7 x 6 – 42 = 42 – 42 = 0,
If x = 7, then
y = 7 x 7 – 42 – 49 – 42 = -7
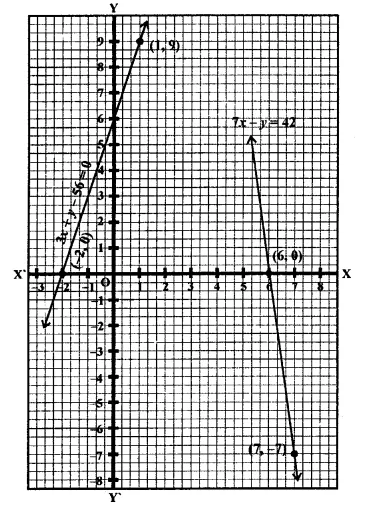
Plot the points (6, 0) (7, -7) on the graph and join them.
After 3 years,
age of Aarushi = x + 3
and age of Ravish = y + 3
⇒ y + 3 = 3(x + 3)
⇒ y + 3 = 3x + 9
⇒ y = 3x+ 9-3
⇒ y = 3x + 6
If x = -2, then y = 3 x (-2) + 6 =6-6=0
If x = 1, then y = 3 x (1) + 6 =3+6=9
Plot the points (1, 9), (-2, 0) on the graph Arundeep’s Mathematics (R.D.) 9th and join them to get another line.
Question 21.
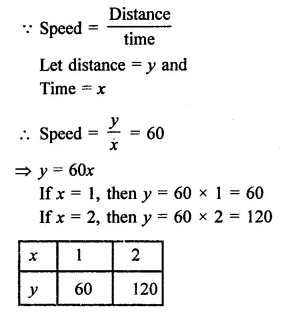
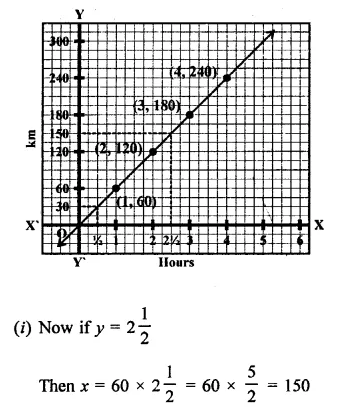
Aarushi was driving a car with a uniform speed of 60 km/h. Draw the distance-time graph. From the graph, find the distance traveled by Aarushi in.
(i) 212 Hours
(ii) 12 Hour
Solution:
Speed of car = 60 km / h.
Now plot the points (60, 1), (120, 2) are the graph and join them to get the graph of the line.
From the graph, we see that
This is the complete blog of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3. To know more about the CBSE Class 9 Maths exam, ask in the comments.
FAQs on RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3
Can I access the RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3 PDF offline?
Once you have downloaded the PDF of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3 online, you can access it offline as well.
From where can I download the PDF of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3?
You can find the download of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3 link from the above blog.
How much does it cost to download the PDF of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3?
You can download the PDF of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Exercise 7.3 for free.