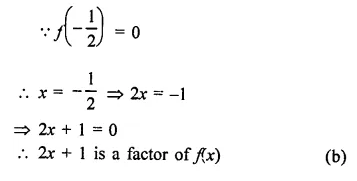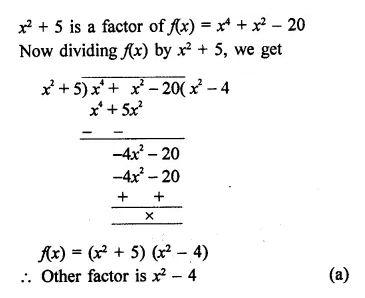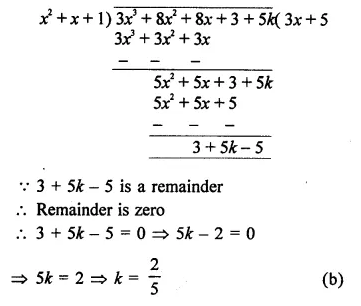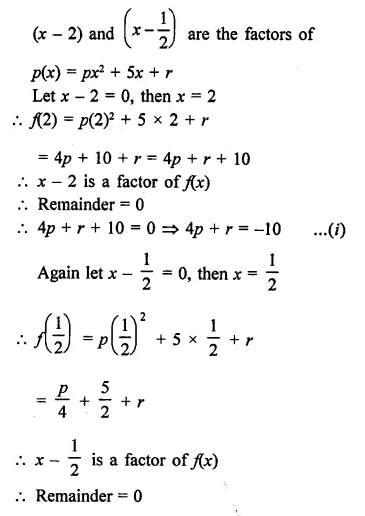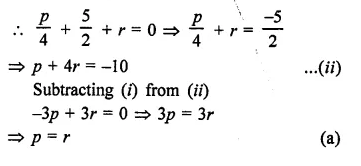RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCQs: Want to become the topper of your Maths class? Choosing the perfect study book is necessary and for that, you can always look up to RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Maths. Be it your class tests or assignments, you can always count on us. To know more about the RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCQs, read the whole blog.
Access answers of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCQs
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
Question 1.
If x – 2 is a factor of x2 + 3 ax – 2a, then a =
(a) 2
(b) -2
(c) 1
(d) -1
Solution:
∴ x – 2 is a factor of
f(x) = x2 + 3 ax – 2a
∴ Remainder = 0
Let x – 2 = 0, then x = 2
Now f(2) = (2)2 + 3a x 2 – 2a
= 4 + 6a – 2a = 4 + 4a
∴ Remainder = 0
∴ 4 + 4a = 0 ⇒ 4a = -4
⇒ a = −44 = -1
∴ a= -1 (d)
Question 2.
If x3 + 6x2 + 4x + k is exactly divisible by x + 2, then k =
(a) -6
(b) -7
(c) -8
(d) -10
Solution:
f(x) – x3 + 6x2 + 4x + k is divisible by x + 2
∴ Remainder = 0
Let x + 2 = 0, then x = -2
∴ f(-2) = (-2)3 + 6(-2)2 + 4(-2) + k
= -8 + 24-8 + k = 8 + k
∴ x + 2 is a factor
∴ Remainder = 0.
⇒ 8 + k= 0 ⇒ k = -8
k = -8 (c)
Question 3.
If x – a is a factor of x3 – 3x2 a + 2a2x + b, then the value of b is
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 3
Solution:
∴ x – a is a factor of x3 – 3x2 a + 2a2x + b
Let f(x) = x3 – 3x2 a + 2a2x+ b
and x – a = 0, then x = a
f(a) = a3 – 3a2.a + 2a2.a + b
= a3 – 3a3 + 2a3 + b = b
∵ x – a is a factor of f(x)
∴ b = 0 (a)
Question 4.
If x140 + 2x151 + k is divisible by x + 1, then the value of k is
(a) 1
(b) -3
(c) 2
(d) -2
Solution:
∴ x + 1 is a factor of f(x) = x140 + 2x151 + k
∴ The remainder will be zero
Let x + 1 = 0, then x = -1
∴ f(-1) = (-1)140 + 2(-1)151 + k
= 1 + 2 x (-1) + k {∵ 140 is even and 151 is odd}
=1-2+k=k-1
∵ Remainder = 0
∴ k – 1=0 ⇒ k=1 (a)
Question 5.
If x + 2 is a factor of x2 + mx + 14, then m =
(a) 7
(b) 2
(c) 9
(d) 14
Solution:
x + 2 is a factor of(x) = x2 + mx + 14
Let x + 2 = 0, then x = -2
f(-2) = (-2)2 + m{-2) + 14
= 4 – 2m + 14 = 18 – 2m
∴ x + 2 is a factor of f(x)
∴ Remainder = 0
⇒ 18 – 2m = 0
2m = 18 ⇒ m = 182 = 9 (c)
Question 6.
If x – 3 is a factor of x2 – ax – 15, then a =
(a) -2
(b) 5
(c) -5
(d) 3
Solution:
x – 3 is a factor of(x) = x2 – ax – 15
Let x – 3 = 0, then x = 3
∴ f(3) = (3)2 – a(3) – 15
= 9 -3a- 15
= -6 -3a
∴ x – 3 is a factor
∴ Remainder = 0
-6 – 3a = 0 ⇒ 3a = -6
∴ a = −63 = -2 (a)
Question 7.
If x51 + 51 is divided by x + 1, the remainder is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 49
(d) 50
Solution:
Left(x) = x51 + 51 is divisible by x + 1
Let x+1=0, then x = -1
∴ f(-1) = (-1)51 + 51 =-1+51 (∵ power 51 is an odd integer)
= 50 (d)
Question 8.
If x+ 1 is a factor of the polynomial 2x2 + kx, then k =
(a) -2
(b) -3
(c) 4
(d) 2
Solution:
∴ x + 1 is a factor of the polynomial 2x2 + kx
Let x+1=0, then x = -1
Now f(x) = 2x2 + kx
∴ Remainder =f(-1) = 0
= 2(-1)2 + k(-1)
= 2 x 1 + k x (-1) = 2 – k
∴ x + 1 is a factor of f(x)
∴ Remainder = 0
∴ 2 – k = 0 ⇒ k = 2 (d)
Question 9.
If x + a is a factor of x4 – a2x2 + 3x – 6a, then a =
(a) 0
(b) -1
(c) 1
(d) 2
Solution:
x + a is a factor o f(x) = x4– a2x2 + 3x – 6a
Let x + a = 0, then x = -a
Now, f(-a) – (-a)4 -a2(-a)2 + 3 (-a) – 6a
= a4-a4-3a-6a = -9a
∴ x + a is a factor of f(x)
∴Remainder = 0
∴ -9a = 0 ⇒ a = 0 (a)
Question 10.
The value of k for which x – 1 is a factor of 4x3 + 3x2 – 4x + k, is
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) -2
(d) -3
Solution:
x- 1 is a factor of f(x) = 4x3 + 3x2 – 4x + k
Let x – 1 = 0, then x = 1
f(1) = 4(1 )3 + 3(1)2 – 4 x 1 + k
= 4+3-4+k=3+k
∴ x- 1 is a factor of f(x)
∴ Remainder = 0
∴ 3 + k = 0 ⇒ k = -3 (d)
Question 11.
If x+2 and x-1 are the factors of x3+ 10x2 + mx + n, then the values of m and n are respectively
(a) 5 and-3
(b) 17 and-8
(c) 7 and-18
(d) 23 and -19
Solution:
x+ 2 and x – 1 are the factors of
f(x) = x3 + 10x2 + mx + n
Let x + 2 = 0, then x = -2
∴ f(-2) = (-2)3 + 10(-2)2 + m(-2) + n
= -8 + 40 – 2m + n = 32 – 2m + n
∴ x + 2 is a factor of f(x)
∴ Remainder = 0
∴ 32 – 2m + n = 0 ⇒ 2m – n = 32 …(i)
Again x – 1 is a factor of f(x)
Let x-1=0, then x= 1
∴ f(1) = (1)3 + 10(1)2 + m x 1 +n
= 1 + 10+ m + n =m + n+11
∴ x- 1 is a factor of f(x)
∴ m + n+ 11=0 ⇒ m+n =-11 …(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii),
3m = 32 – 11 = 21
⇒ m = 213 = 7
and n = -11 – m = m = 7, n = -18
∴ m= 7, n = -18 (c)
Question 12.
Let f(x) be a polynomial such that f( −12 )= 0, then a factor of f(x) is
(a) 2x – 1
(b) 2x + b
(c) x- 1
(d) x + 1
Solution:
Question 13.
When x3 – 2x2 + ax – b is divided by x2 – 2x-3, the remainder is x – 6. The value of a and b are respectively.
(a) -2, -6
(b) 2 and -6
(c) -2 and 6
(d) 2 and 6
Solution:
Let f(x) = x3 – 2x2 + ax – b
and Dividing f(x) by x2 – 2x + 3
Remainder = x – 6
Let p(x) = x3 – 2x2 + ax – b – (x – 6) or x3 – 2x2 + x(a – 1) – b + 6 is divisible by x2 – 2x+ 3 exactly
Now, x2-2x-3 = x2-3x + x- 3
= x(x – 3) + 1(x – 3)
= (x – 3) (x + 1)
∴ x – 3 and x + 1 are the factors of p(x)
Let x – 3 = 0, then x = 3
∴ p(3) = (3)3 – 2(3)2 + (a-1)x3-b + 6
= 27-18 + 3a-3-b + 6
= 33-21+3 a-b
= 12 + 3 a-b
∴ x – 3 is a factor
∴ 12 + 3a-b = 0 ⇒ 3a-b = -12 …(i)
Again let x + 1 = 0, then x = -1
∴p(-1) = (-1)3 – 2(-l)2 + (a – 1) X (-1) – b + 6
= -1-2 + 1 – a – 6 + 6
= 4 – a- b
∴ x + 1 is a factor
4-a-b = 0 ⇒ a + b = 4 …(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii),
4 a = -12 + 4 = -8 ⇒ a = −84 = -2
From (ii),
and -2 + 6 = 4⇒ 6 = 4 + 2 = 6
∴ a = -2, h = 6 (b)
Question 14.
One factor of x4 + x2 – 20 is x2 + 5, the other is
(a) x2 – 4
(b) x – 4
(c) x2-5
(d) x + 4
Solution:
Question 15.
If (x – 1) is a factor of polynomial fix) but not of g(x), then it must be a factor of
(a) f(x) g(x)
(b) -f(x) + g(x)
(c) f(x) – g(x)
(d) {f(x) + g(x)}g(x)
Solution:
∴ (x – 1) is a factor of a polynomial f(x)
But not of a polynomial g(x)
∴ (x – 1) will be the factor of the product of f(x) and g(x) (a)
Question 16.
(x + 1) is a factor of xn + 1 only if
(a) n is an odd integer
(b) n is an even integer
(c) n is a negative integer
(d) n is a positive integer
Solution:
∴ (x + 1) is a factor of xn+ 1
Let x + 1 = 0, then x = -1
∴ f(x) = xn + 1
and f(-1) = (-1)n + 1
But (-1)n is positive if n is an even integer and negative if n is an odd integer and (-1)n +1=0 {∵ x + 1 is a factor of(x)}
(-1)n must be negative
∴ n is an odd integer (a)
Question 17.
If x2 + x + 1 is a factor of the polynomial 3x3 + 8x2 + 8x + 3 + 5k, then the value of k is
(a) 0
(b) 25
(c) 52
(d) -1
Solution:
x2 + x + 1 is a factor of
f(x) = 3x3 + 8x2 + 8x + 3 + 5k
Now dividing by x2 + x + 1, we get
Question 18.
If (3x – 1)7 = a7x7 + a6x6 + a5x5 + … + a1x + a0, then a7 + a6 + a5 + … + a1 + a0 =
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 128
(d) 64
Solution:
f(x) = [3(1) – 1]7 = a7x7 + a6x6 + a5x5 + … + a1x + a0
Let x = 1, then
f(1) = (3x- 1)7 = a7(1)7 + a6(1)6 + a5(1)5 + … + a1 x 1 + a0
⇒ (3 – 1)7 = a7 x 1 + a6 x 1+ a5 x 1 + … + a1x 1 +a0
⇒ (2)7 = a7 + a6 + a5 + … + a1 +a0
∴ a7 + a6 + a5 + … + a1 + a0= 128 (c)
Question 19.
If both x – 2 and x – 12 are factors of px2 + 5x + r, then
(a) p = r
(b) p + r = 0
(c) 2p + r = 0
(d) p + 2r = 0
Solution:
Question 20.
If x2 – 1 is a factor of ax4 + bx3 + cx2 + dx + e, then
(a) a + c + e- b + d
(b)a + b + e = c + d
(c)a + b + c = d+ e
(d)b + c + d= a + e
Solution:
X2 – 1 is a factor of ax4 + bx3 + cx2 + dx + e
⇒ (x + 1), (x – 1) are the factors of ax4 + bx3 + cx2 + dx + e
Let f(x) = ax4 + bx3 + cx2 + dx + e
and x + 1 = 0 then x = -1
∴ f(-1) = a(-1)4 + b(-1)3 + c(-1)2 + d(-1) + e
= a- b + c- d+ e
∴ x + 1 is a factor of f(x)
∴ a-b + c- d+e = 0
⇒ a + c + e = b + d (a)
This is the complete blog on RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCqs. To know more about the CBSE Class 9 Maths exam, ask in the comments.
FAQs on RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCqs
How many questions are there in RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCQs?
There are 20 questions in RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCQs.
Is it even beneficial to study RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCQs?
Yes, your preparation will be strengthened with this amazing help book. All your questions will be answered by this book.
Are the solutions RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 6 MCQs relevant?
The solutions are relevant as they are designed by the subject matter experts.