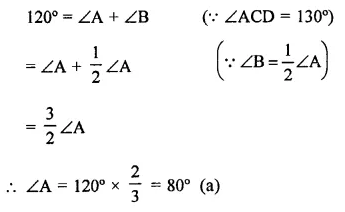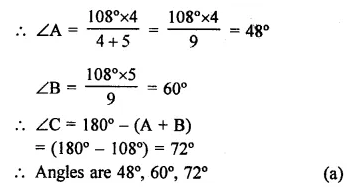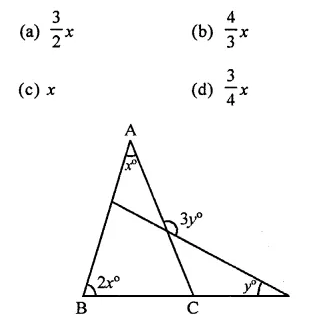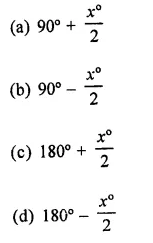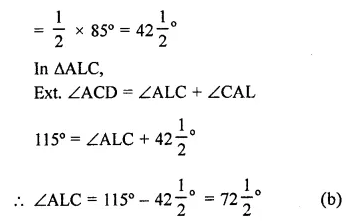RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs: Attempting an Objective type can be quite tricky for some. But you don’t have to worry as we have RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs for you. All the MCQs are solved in an easy and understandable manner. You can find other exercises solutions in the RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Maths. To know more about RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs, read the whole blog.
Access answers of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
Question 1.
If all the three angles of a triangle are equal, then each one of them is equal to
(a) 90°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 30°
Solution:
∵ Sum of three angles of a triangle = 180°
∴ Each angle = 180∘3 = 60° (c)
Question 2.
If two acute angles of a right triangle are equal, then each acute is equal to
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Solution:
In a right triangle, one angle = 90°
∴ Sum of other two acute angles = 180° – 90° = 90°
∵ Both angles are equal
∴ Each angle will be = 90∘2 = 45° (b)
Question 3.
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to 100° and two interior opposite angles are equal. Each of these angles is equal to
(a) 75°
(b) 80°
(c) 40°
(d) 50°
Solution:
In a triangle, exterior angles is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angles
∴ Sum of interior opposite angles = 100°
∵ Both angles are equal
∴ Each angle will be = 100∘2 = 50° (d)
Question 4.
If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then the triangle is
(a) an isosceles triangle
(b) an obtuse triangle
(c) an equilateral triangle
(d) a right triangle
Solution:
Let ∠A, ∠B, ∠C be the angles of a ∆ABC and let ∠A = ∠B + ∠C
But ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
( Sum of angles of a triangle)
∴ ∠A + ∠A = 180° ⇒ 2∠A = 180°
⇒ ∠A = 180∘2 = 90°
∴ ∆ is a right triangle (d)
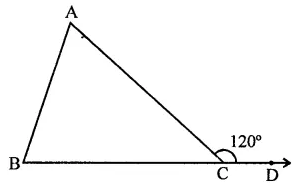
Question 5.
Side BC of a triangle ABC has been produced to a point D such that ∠ACD = 120°. If ∠B = 12∠A, then ∠A is equal to
(a) 80°
(b) 75°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Solution:
Side BC of ∆ABC is produced to D, then
Ext. ∠ACB = ∠A + ∠B
(Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angles)
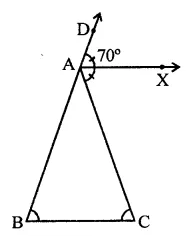
Question 6.
In ∆ABC, ∠B = ∠C and ray AX bisects the exterior angle ∠DAC. If ∠DAX = 70°, then ∠ACB =
(a) 35°
(b) 90°
(c) 70°
(d) 55°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, ∠B = ∠C
AX is the bisector of ext. ∠CAD
∠DAX = 70°
∴ ∠DAC = 70° x 2 = 140°
But Ext. ∠DAC = ∠B + ∠C
= ∠C + ∠C (∵ ∠B = ∠C)
= 2∠C
∴ 2∠C = 140° ⇒ ∠C = 140∘2 = 70°
∴ ∠ACB = 70° (c)
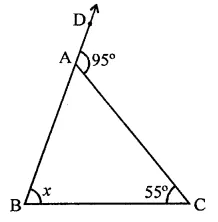
Question 7.
In a triangle, an exterior angle at a vertex is 95° and its one of the interior opposite angle is 55°, then the measure of the other interior angle is
(a) 55°
(b) 85°
(c) 40°
(d) 9.0°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, BA is produced to D such that ∠CAD = 95°
and let ∠C = 55° and ∠B = x°
∵ Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of its opposite interior angle
∴ ∠CAD = ∠B + ∠C ⇒ 95° = x + 55°
⇒ x = 95° – 55° = 40°
∴ Other interior angle = 40° (c)
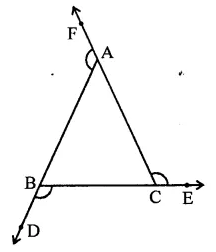
Question 8.
If the sides of a triangle are produced in order, then the sum of the three exterior angles so formed is
(a) 90°
(b) 180°
(c) 270°
(d) 360°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, sides AB, BC and CA are produced in order, then exterior ∠FAB, ∠DBC and ∠ACE are formed
We know an exterior angles of a triangle is equal to the sum of its interior opposite angles
∴ ∠FAB = ∠B + ∠C
∠DBC = ∠C + ∠A and
∠ACE = ∠A + ∠B Adding we get,
∠FAB + ∠DBC + ∠ACE = ∠B + ∠C + ∠C + ∠A + ∠A + ∠B
= 2(∠A + ∠B + ∠C)
= 2 x 180° (Sum of angles of a triangle)
= 360° (d)
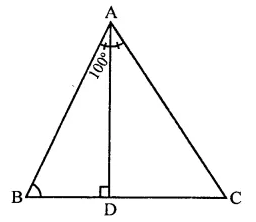
Question 9.
In ∆ABC, if ∠A = 100°, AD bisects ∠A and AD⊥ BC. Then, ∠B =
(a) 50°
(b) 90°
(c) 40°
(d) 100°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 100°
AD is bisector of ∠A and AD ⊥ BC
Now, ∠BAD = 100∘2 = 50°
In ∆ABD,
∠BAD + ∠B + ∠D= 180°
(Sum of angles of a triangle)
⇒ ∠50° + ∠B + 90° = 180°
∠B + 140° = 180°
⇒ ∠B = 180° – 140° ∠B = 40° (c)
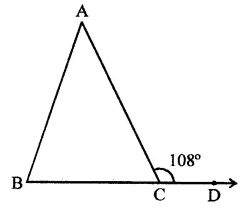
Question 10.
An exterior angle of a triangle is 108° and its interior opposite angles are in the ratio 4:5. The angles of the triangle are
(a) 48°, 60°, 72°
(b) 50°, 60°, 70°
(c) 52°, 56°, 72°
(d) 42°, 60°, 76°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, BC is produced to D and ∠ACD = 108°
Ratio in ∠A : ∠B = 4:5
∵ Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of its opposite interior angles
∴ ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B = 108°
Ratio in ∠A : ∠B = 4:5
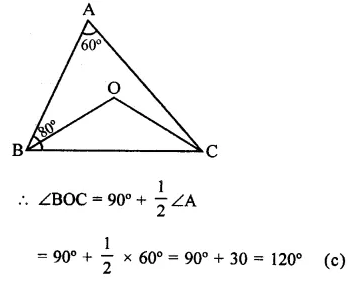
Question 11.
In a ∆ABC, if ∠A = 60°, ∠B = 80° and the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at O, then ∠BOC =
(a) 60°
(b) 120°
(c) 150°
(d) 30°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 60°, ∠B = 80°
∴ ∠C = 180° – (∠A + ∠B)
= 180° – (60° + 80°)
= 180° – 140° = 40°
Bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at O
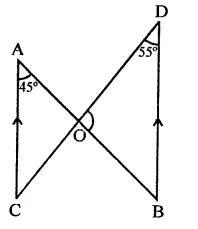
Question 12.
Line segments AB and CD intersect at O such that AC || DB. If ∠CAB = 45° and ∠CDB = 55°, then ∠BOD =
(a) 100°
(b) 80°
(c) 90°
(d) 135°
Solution:
In the figure,
AB and CD intersect at O
and AC || DB, ∠CAB = 45°
and ∠CDB = 55°
∵ AC || DB
∴ ∠CAB = ∠ABD (Alternate angles)
In ∆OBD,
∠BOD = 180° – (∠CDB + ∠ABD)
= 180° – (55° + 45°)
= 180° – 100° = 80° (b)
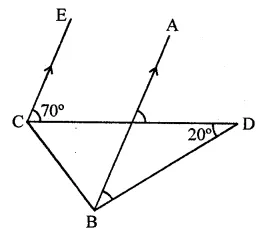
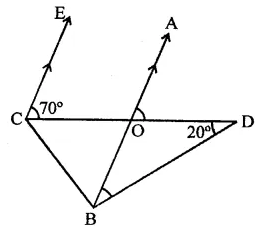
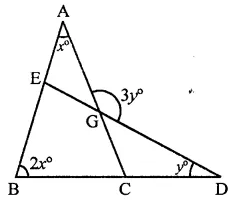
Question 13.
In the figure, if EC || AB, ∠ECD = 70° and ∠BDO = 20°, then ∠OBD is
(a) 20°
(b) 50°
(c) 60°
(d) 70°
Solution:
In the figure, EC || AB
∠ECD = 70°, ∠BDO = 20°
∵ EC || AB
∠AOD = ∠ECD (Corresponding angles)
⇒ ∠AOD = 70°
In ∆OBD,
Ext. ∠AOD = ∠OBD + ∠BDO
70° = ∠OBD + 20°
⇒ ∠OBD = 70° – 20° = 50° (b)
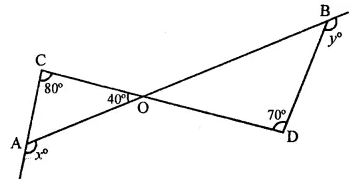
Question 14.
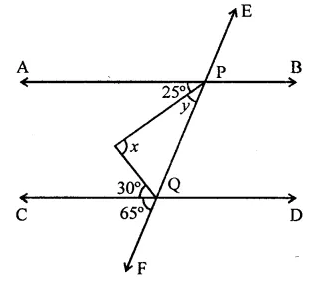
In the figure, x + y =
(a) 270
(b) 230
(c) 210
(d) 190°
Solution:
In the figure
Ext. ∠OAE = ∠AOC + ∠ACO
⇒ x = 40° + 80° = 120°
Similarly,
Ext. ∠DBF = ∠ODB + ∠DOB
y = 70° + ∠DOB
[(∵ ∠AOC = ∠DOB) (vertically opp. angles)]
= 70° + 40° = 110°
∴ x+y= 120°+ 110° = 230° (b)
Question 15.
If the measures of angles of a triangle are in the ratio of 3 : 4 : 5, what is the measure of the smallest angle of the triangle?
(a) 25°
(b) 30°
(c) 45°
(d) 60°
Solution:
Ratio in the measures of the triangle =3:4:5
Sum of angles of a triangle = 180°
Let angles be 3x, 4x, 5x
Sum of angles = 3x + 4x + 5x = 12x
∴ Smallest angle = 180x3x12x = 45° (c)
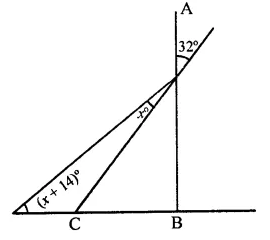
Question 16.
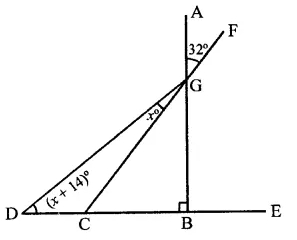
In the figure, if AB ⊥ BC, then x =
(a) 18
(b) 22
(c) 25
(d) 32
Solution:
In the figure, AB ⊥ BC
∠AGF = 32°
∴ ∠CGB = ∠AGF (Vertically opposite angles)
= 32°
In ∆GCB, ∠B = 90°
∴ ∠CGB + ∠GCB = 90°
⇒ 32° + ∠GCB = 90°
⇒ ∠GCB = 90° – 32° = 58°
Now in ∆GDC,
Ext. ∠GCB = ∠CDG + ∠DGC
⇒ 58° = x + 14° + x
⇒ 2x + 14° = 58°
⇒ 2x = 58 – 14° = 44
⇒ x = 442 = 22°
∴ x = 22° (b)
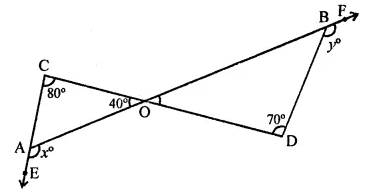
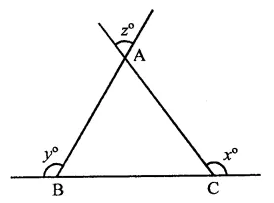
Question 17.
In the figure, what is ∠ in terms of x and y?
(a) x + y + 180
(b) x + y – 180
(c) 180° -(x+y)
(d) x+y + 360°
Solution:
In the figure, BC is produced both sides CA and BA are also produced
In ∆ABC,
∠B = 180° -y
and ∠C 180° – x
∴ z = ∠A = 180° – (B + C)
= 180° – (180 – y + 180 -x)
= 180° – (360° – x – y)
= 180° – 360° + x + y = x + y – 180° (b)
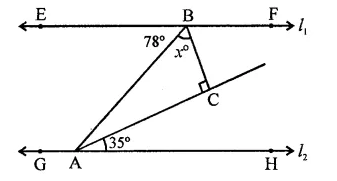
Question 18.
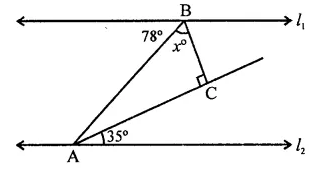
In the figure, for which value of x is l1 || l2?
(a) 37
(b) 43
(c) 45
(d) 47
Solution:
In the figure, l1 || l2
∴ ∠EBA = ∠BAH (Alternate angles)
∴ ∠BAH = 78°
⇒ ∠BAC + ∠CAH = 78°
⇒ ∠BAC + 35° = 78°
⇒ ∠BAC = 78° – 35° = 43°
In ∆ABC, ∠C = 90°
∴ ∠ABC + ∠BAC = 90°
⇒ x + 43° = 90° ⇒ x = 90° – 43°
∴ x = 47° (d)
Question 19.
In the figure, what is y in terms of x?
Solution:
In ∆ABC,
∠ACB = 180° – (x + 2x)
= 180° – 3x …(i)
and in ∆BDG,
∠BED = 180° – (2x + y) …(ii)
∠EGC = ∠AGD (Vertically opposite angles)
= 3y
In quad. BCGE,
∠B + ∠ACB + ∠CGE + ∠BED = 360° (Sum of angles of a quadrilateral)
⇒ 2x+ 180° – 3x + 3y + 180°- 2x-y = 360°
⇒ -3x + 2y = 0
⇒ 3x = 2y ⇒ y = 32x (a)
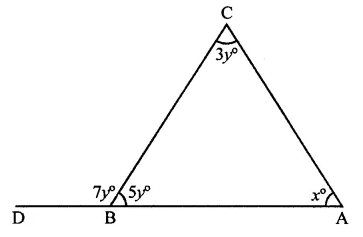
Question 20.
In the figure, what is the value of x?
(a) 35
(b) 45
(c) 50
(d) 60
Solution:
In the figure, side AB is produced to D
∴ ∠CBA + ∠CBD = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ 7y + 5y = 180°
⇒ 12y = 180°
⇒ y = 18012 = 15
and Ext. ∠CBD = ∠A + ∠C
⇒ 7y = 3y + x
⇒ 7y -3y = x
⇒ 4y = x
∴ x = 4 x 15 = 60 (d)
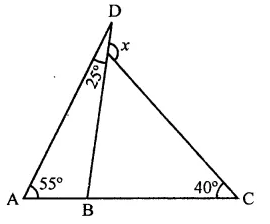
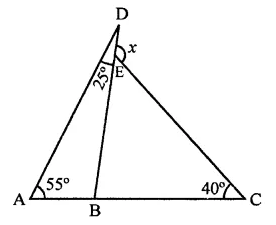
Question 21.
In the figure, the value of x is
(a) 65°
(b) 80°
(c) 95°
(d) 120°
Solution:
In the figure, ∠A = 55°, ∠D = 25° and ∠C = 40°
Now in ∆ABD,
Ext. ∠DBC = ∠A + ∠D
= 55° + 25° = 80°
Similarly, in ∆BCE,
Ext. ∠DEC = ∠EBC + ∠ECB
= 80° + 40° = 120° (d)
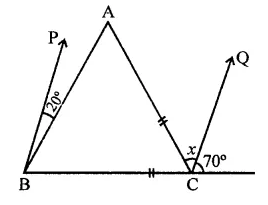
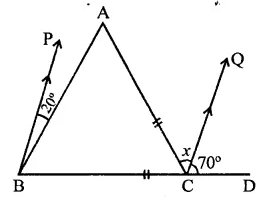
Question 22.
In the figure, if BP || CQ and AC = BC, then the measure of x is
(a) 20°
(b) 25°
(c) 30°
(d) 35°
Solution:
In the figure, AC = BC, BP || CQ
∵ BP || CQ
∴ ∠PBC – ∠QCD
⇒ 20° + ∠ABC = 70°
⇒ ∠ABC = 70° – 20° = 50°
∵ BC = AC
∴ ∠ACB = ∠ABC (Angles opposite to equal sides)
= 50°
Now in ∆ABC,
Ext. ∠ACD = ∠B + ∠A
⇒ x + 70° = 50° + 50°
⇒ x + 70° = 100°
∴ x = 100° – 70° = 30° (c)
Question 23.
In the figure, AB and CD are parallel lines and transversal EF intersects them at P and Q respectively. If ∠APR = 25°, ∠RQC = 30° and ∠CQF = 65°, then
(a) x = 55°, y = 40°
(b) x = 50°, y = 45°
(c) x = 60°, y = 35°
(d) x = 35°, y = 60°
Solution:
In the figure,
∵ AB || CD, EF intersects them at P and Q respectively,
∠APR = 25°, ∠RQC = 30°, ∠CQF = 65°
∵ AB || CD
∴ ∠APQ = ∠CQF (Corresponding anlges)
⇒ y + 25° = 65°
⇒ y = 65° – 25° = 40°
and APQ + PQC = 180° (Co-interior angles)
y + 25° + ∠1 +30°= 180°
40° + 25° + ∠1 + 30° = 180°
⇒ ∠1 + 95° = 180°
∴ ∠1 = 180° – 95° = 85°
Now, ∆PQR,
∠RPQ + ∠PQR + ∠PRQ = 180° (Sum of angles of a triangle)
⇒ 40° + x + 85° = 180°
⇒ 125° + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° – 125° = 55°
∴ x = 55°, y = 40° (a)
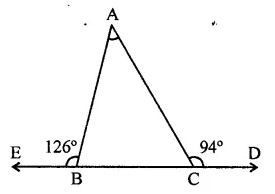
Question 24.
The base BC of triangle ABC is produced both ways and the measure of exterior angles formed are 94° and 126°. Then, ∠BAC = ?
(a) 94°
(b) 54°
(c) 40°
(d) 44°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, base BC is produced both ways and ∠ACD = 94°, ∠ABE = 126°
Ext. ∠ACD = ∠BAC + ∠ABC
⇒ 94° = ∠BAC + ∠ABC
Similarly, ∠ABE = ∠BAC + ∠ACB
⇒ 126° = ∠BAC + ∠ACB
Adding,
94° + 126° = ∠BAC + ∠ABC + ∠ACB + ∠BAC
220° = 180° + ∠BAC
∴ ∠BAC = 220° -180° = 40° (c)
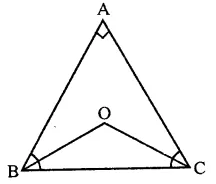
Question 25.
If the bisectors of the acute angles of a right triangle meet at O, then the angle at O between the two bisectors is
(a) 45°
(b) 95°
(c) 135°
(d) 90°
Solution:
In right ∆ABC, ∠A = 90°
Bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at O, then 1
∠BOC = 90° + 12 ∠A
= 90°+ 12 x 90° = 90° + 45°= 135° (c)
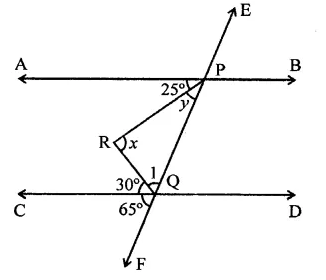
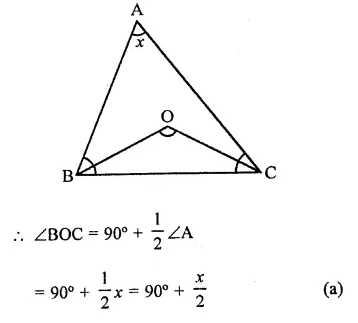
Question 26.
The bisects of exterior angles at B and C of ∆ABC, meet at O. If ∠A = .x°, then ∠BOC=
Solution:
In ∆ABC, ∠A = x°
and bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at O.
Question 27.
In a ∆ABC, ∠A = 50° and BC is produced to a point D. If the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACD meet at E, then ∠E =
(a) 25°
(b) 50°
(c) 100°
(d) 75°
Solution:
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 50°
BC is produced
Bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACD meet at ∠E
∴ ∠E = 12 ∠A = 12 x 50° = 25° (a)
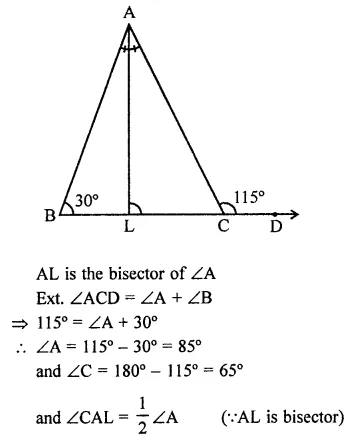
Question 28.
The side BC of AABC is produced to a point D. The bisector of ∠A meets side BC in L. If ∠ABC = 30° and ∠ACD =115°,then ∠ALC =
(a) 85°
(b) 7212 °
(c) 145°
(d) none of these
Solution:
In ∆ABC, BC is produced to D
∠B = 30°, ∠ACD = 115°
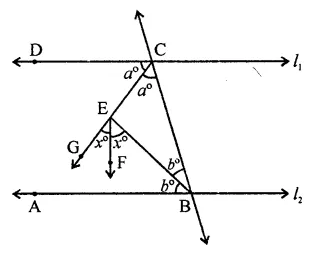
Question 29.
In the figure , if l1 || l2, the value of x is
(a) 22 12
(b) 30
(c) 45
(d) 60
Solution:
In the figure, l1 || l2
EC, EB are the bisectors of ∠DCB and ∠CBA respectively EF is the bisector of ∠GEB
∵ EC and EB are the bisectors of ∠DCB and ∠CBA respectively
∴ ∠CEB = 90°
∴ a + b = 90° ,
and ∠GEB = 90° (∵ ∠CEB = 90°)
2x = 90° ⇒ x = 902 = 45 (c)
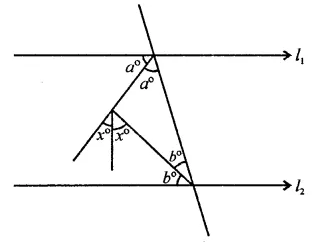
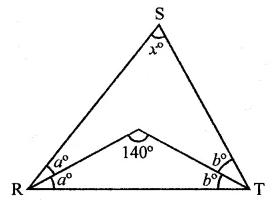
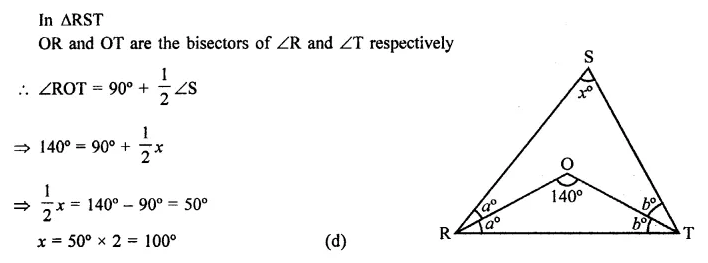
Question 30.
In ∆RST (in the figure), what is the value of x?
(a) 40°
(b) 90°
(c) 80°
(d) 100°
Solution:
This is the complete blog on RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs. To know more about the CBSE Class 9 Maths exams, ask in the comments.
FAQs on RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs
How many questions are there in RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs?
There are 30 questions in RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions for Chapter 1 MCQs.
Is it even beneficial to study RD Sharma for Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs?
Yes, your preparation will be strengthened with this amazing help book. All your questions will be answered by this book.
Are the solutions RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs relevant?
The solutions of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 MCQs are relevant as they are designed by the subject matter experts.